Diving into the complex world of wealth distribution, this exploration of Understanding wealth inequality delves into the economic, social, and political factors that play a role in shaping the disparities we see today. From historical events to the impact on society, this topic opens up a dialogue on the various dimensions of wealth inequality.
With a critical lens, we’ll navigate through the effects of wealth inequality on access to essential services, the potential solutions to bridge the gap, and how intersecting factors like race, gender, and social backgrounds further complicate the issue. Strap in for a ride as we unravel the layers of Understanding wealth inequality.
Factors contributing to wealth inequality
Wealth inequality is influenced by a variety of economic, social, and political factors that shape the distribution of resources and opportunities within societies.
Economic Factors
- The concentration of wealth among a small percentage of the population leads to widening wealth gaps.
- Globalization and technological advancements have contributed to the rise of high-skill, high-wage jobs, leaving low-skilled workers behind.
- Tax policies and financial regulations can either exacerbate or mitigate wealth inequality.
Social Factors
- Historical events such as slavery, colonization, and discrimination have created intergenerational wealth disparities that persist today.
- Social mobility barriers, such as access to quality education and healthcare, limit opportunities for wealth accumulation among disadvantaged groups.
- Cultural norms and social networks can influence access to resources and economic opportunities.
Political Factors
- Government policies on taxation, welfare, and labor rights play a crucial role in wealth distribution.
- Corporate influence in politics can lead to policies that benefit the wealthy elite at the expense of the working class.
- The lack of regulatory oversight can result in monopolistic practices that concentrate wealth in the hands of a few.
Role of Education
- Access to quality education can level the playing field and reduce wealth inequality by providing individuals with the skills and knowledge needed to succeed in the workforce.
- Disparities in education funding and resources can perpetuate wealth gaps between affluent and low-income communities.
- Investing in lifelong learning and vocational training programs can help bridge the skills gap and promote economic mobility.
Wealth Distribution by Region
- Countries with higher levels of income inequality tend to have greater wealth disparities among their populations.
- Nordic countries like Sweden and Denmark have implemented progressive tax policies and social welfare programs that reduce wealth inequality.
- Developing nations often struggle with extreme wealth inequality due to factors such as corruption, lack of infrastructure, and limited access to education.
Effects of wealth inequality on society
Wealth inequality has profound effects on various aspects of society, impacting access to essential services, social mobility, crime rates, and overall psychological well-being.
Access to Healthcare, Education, and Opportunities
Wealth inequality significantly affects access to healthcare, education, and opportunities. Those with higher wealth have better access to quality healthcare services, prestigious educational institutions, and lucrative opportunities, while individuals with lower wealth struggle to afford basic necessities and access the same level of resources.
Social Mobility
- Wealth disparity hinders social mobility, making it challenging for individuals from lower-income backgrounds to move up the economic ladder. Limited access to resources and opportunities perpetuates the cycle of poverty and restricts upward mobility.
-
Individuals born into poverty are more likely to remain in poverty throughout their lives, facing obstacles in accessing quality education, securing stable employment, and building wealth.
Correlation Between Wealth Inequality and Crime Rates
- Wealth inequality is closely linked to higher crime rates in society. Areas with significant wealth disparities often experience higher levels of crime, as individuals facing economic hardships may resort to illegal activities to meet their basic needs.
-
Studies have shown that neighborhoods with pronounced wealth inequality are more likely to have increased rates of property crime, violent crime, and social unrest.
Psychological Effects of Living in a Society with High Wealth Inequality
- The psychological effects of living in a society with high wealth inequality can be detrimental to individuals’ well-being. Feelings of inadequacy, envy, and stress may arise when individuals compare their financial status to others who are significantly wealthier.
-
Moreover, the sense of unfairness and lack of opportunities can lead to a sense of hopelessness and decreased mental health among those experiencing the impacts of wealth inequality.
Solutions to address wealth inequality
Addressing wealth inequality requires a multi-faceted approach involving policies and programs that aim to level the playing field and provide opportunities for all individuals to achieve economic success.
Progressive taxation
Progressive taxation is a key tool in addressing wealth gaps by imposing higher tax rates on individuals with higher incomes. This approach helps redistribute wealth more equitably and ensures that those who can afford to pay more contribute their fair share to society.
Wealth redistribution programs
Wealth redistribution programs such as social welfare initiatives, affordable housing projects, and education subsidies can help bridge the wealth gap by providing support to individuals and families in need. These programs aim to lift people out of poverty and provide them with the resources they need to thrive.
Universal basic income
Universal basic income (UBI) is a concept that involves providing all citizens with a guaranteed income to cover basic living expenses. By ensuring that everyone has a financial safety net, UBI can help reduce poverty, promote economic stability, and address wealth inequality. It gives individuals the freedom to pursue opportunities without the fear of financial insecurity.
Intersections of wealth inequality with race, gender, and other social factors
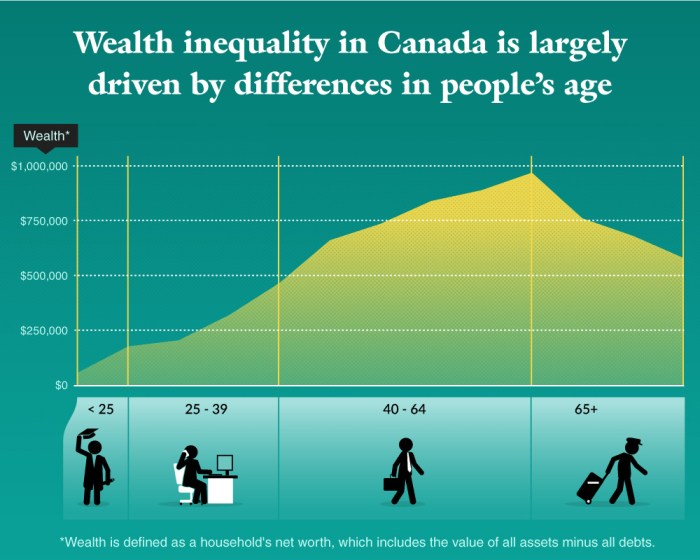
In the United States, wealth inequality is deeply intertwined with race, gender, and other social factors, leading to disparities in economic opportunities and outcomes.
Race and Historical Context
Race has played a significant role in shaping wealth distribution in the U.S. throughout history. Systemic racism, discriminatory policies, and unequal access to resources have perpetuated wealth gaps between racial groups. For example, redlining practices in the mid-20th century restricted home loans to minority communities, preventing them from building generational wealth through homeownership.
Gender and Wealth Distribution
Gender also influences wealth distribution, with women generally earning less than men and facing barriers to wealth accumulation. The gender pay gap, limited access to higher-paying jobs, and societal expectations around caregiving responsibilities contribute to women having less wealth compared to men. This disparity is even more pronounced for women of color.
Other Social Factors and Wealth Gaps
Factors like disability, age, and geographic location further exacerbate wealth inequality. People with disabilities often face challenges in accessing education and employment opportunities, leading to lower income levels and wealth accumulation. Older individuals may struggle to save for retirement, especially if they face age discrimination in the workforce. Geographic disparities in resources and economic opportunities create uneven wealth distribution across regions.
Intersectionality in Wealth Inequality
Intersectionality, a concept introduced by Kimberlé Crenshaw, highlights how various social identities intersect to shape individuals’ experiences of privilege and oppression. In the context of wealth inequality, intersectionality emphasizes that race, gender, disability, age, and other factors do not operate in isolation but interact to create complex dynamics of advantage and disadvantage in wealth accumulation and distribution.
