Get ready to dive into the world of Retirement age statistics, where we uncover the trends and influences shaping this crucial aspect of demographics. From analyzing global variations to understanding the factors driving retirement age decisions, this topic is about to get real interesting.
As we explore the nuances of retirement age statistics, you’ll gain a fresh perspective on how different factors come into play across various countries and demographics.
Overview of Retirement Age Statistics
Retirement age statistics play a crucial role in understanding the shifting demographics of a population. By analyzing these statistics, we can gain insights into the aging workforce, pension systems, and overall economic health of a country.
Variation in Retirement Age across Countries
Retirement age varies significantly from one country to another, influenced by cultural norms, government policies, and economic conditions. For example, some countries have mandatory retirement ages while others allow individuals to work well into their senior years.
Factors Influencing Retirement Age Trends
- Health and Life Expectancy: Longer life expectancies have led to individuals working past traditional retirement ages.
- Economic Stability: Countries with strong economies may have higher retirement ages as individuals can afford to retire later.
- Pension Systems: The structure of pension systems can incentivize or discourage early retirement, impacting overall retirement age trends.
- Cultural Norms: Cultural attitudes towards work and retirement can also influence when individuals choose to retire.
Retirement Age Trends by Gender
In analyzing retirement age statistics, it is important to consider the differences between males and females in terms of when they typically retire. Societal norms and expectations play a significant role in shaping these trends, influencing the retirement decisions of individuals based on their gender.
Gender Disparities in Retirement Age
- In many countries, there is a notable gender gap in retirement age, with women often retiring at a younger age compared to men.
- This difference can be attributed to various factors such as wage disparities, caregiving responsibilities, and societal expectations regarding gender roles.
- For example, in Japan, women tend to retire earlier than men due to cultural norms that prioritize family responsibilities over career advancement.
- Similarly, in some European countries, women retire earlier than men on average, reflecting traditional gender roles that expect women to prioritize family over work.
Factors Influencing Retirement Age
Various factors play a significant role in determining the retirement age of individuals. These factors can range from economic conditions to cultural attitudes and changing work dynamics.
Economic Conditions
Economic conditions, such as job availability, wage levels, and overall financial stability, can greatly impact when individuals choose to retire. In times of economic uncertainty or recession, individuals may delay retirement to secure their financial future.
Healthcare Access
The availability and quality of healthcare services can influence retirement age. Access to affordable healthcare can provide individuals with the confidence to retire earlier, knowing that their medical needs will be taken care of.
Pension Policies
Pension policies, including retirement benefits and savings plans, can also affect when individuals decide to retire. Generous pension schemes may encourage early retirement, while inadequate policies might force individuals to work longer.
Cultural Attitudes and Traditions
Cultural attitudes towards aging and retirement can shape individuals’ decisions regarding when to retire. In some cultures, the concept of retirement may not even exist, leading individuals to work well into old age.
Changing Work Dynamics
The evolving nature of work, such as the rise of remote work and gig economy jobs, can impact retirement age. Some individuals may choose to continue working in a flexible capacity, while others may opt for early retirement due to burnout or job dissatisfaction.
Retirement Age and Life Expectancy
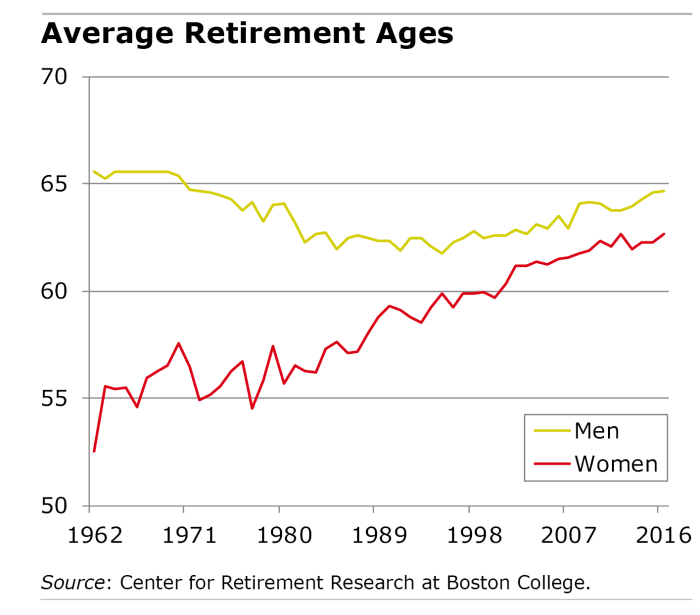
The relationship between retirement age and life expectancy is a crucial factor to consider when planning for retirement. As life expectancy increases, individuals may need to adjust their retirement age to ensure they have enough savings to last them through their older years.
Impact of Increasing Life Expectancy on Retirement Age
- As people are living longer, they may need to work for a longer period to support themselves financially in retirement.
- Increasing life expectancy can also result in higher healthcare costs in old age, leading individuals to delay retirement to save more money.
- In some countries, the retirement age is being adjusted based on life expectancy projections to ensure the sustainability of pension systems.
Countries Adjusting Retirement Age based on Life Expectancy
| Country | Adjustment Policy |
|---|---|
| United Kingdom | The state pension age is regularly reviewed and adjusted based on life expectancy projections. |
| Japan | Implemented a gradual increase in the retirement age to account for the rising life expectancy of its population. |
| Sweden | Introduced a formula linking the retirement age to life expectancy to ensure the sustainability of its pension system. |
