How to analyze stock charts dives into the world of stock market analysis with a fresh perspective, breaking down complex concepts into easy-to-understand insights. Get ready to unlock the secrets of stock charts in a whole new light.
From understanding basic elements to decoding candlestick patterns, this guide will equip you with the tools needed to navigate the dynamic landscape of stock trading like a pro.
Understanding Stock Charts
When it comes to analyzing stocks, understanding stock charts is essential. Stock charts provide a visual representation of a stock’s price movement over a specific period of time. By interpreting these charts, investors can make informed decisions about buying or selling stocks.
Basic Elements of a Stock Chart
- Price: The vertical axis represents the price of the stock, while the horizontal axis represents the time period.
- Volume: The volume bars at the bottom of the chart show the number of shares traded during each time period.
- Candlesticks: Candlestick charts display the open, high, low, and close prices for each time period, providing more detailed information.
Different Types of Stock Charts
- Line Charts: Show the closing prices of a stock over time, providing a simple overview of price trends.
- Bar Charts: Display the high, low, open, and close prices for each time period, offering more detailed information than line charts.
- Candlestick Charts: Widely used by traders to identify patterns and trends in stock prices, providing a comprehensive view of price movements.
Importance of Stock Charts in Analyzing Market Trends
Stock charts are crucial for analyzing market trends as they help investors identify patterns, trends, and potential opportunities in the stock market. By studying stock charts, investors can make informed decisions based on historical price movements and volume trends. This analysis can help predict future price movements and anticipate market changes, ultimately improving investment strategies and maximizing returns.
Technical Analysis Tools
In stock chart analysis, various technical tools are utilized to help traders make informed decisions based on historical price movements.
Moving Averages
Moving averages are commonly used technical analysis tools that smooth out price data to identify trends over a specific period. They help traders understand the direction and strength of a stock’s trend by filtering out short-term fluctuations. There are different types of moving averages, such as simple moving averages (SMA) and exponential moving averages (EMA), each offering unique insights into stock trends.
- Simple Moving Average (SMA): Calculated by adding up a set number of closing prices and dividing by the number of periods. It provides a clearer picture of the overall trend.
- Exponential Moving Average (EMA): Gives more weight to recent price data, making it more responsive to current price movements. It helps traders identify trend changes faster.
Understanding moving averages can help traders spot potential trend reversals or confirm existing trends in stock prices.
Support and Resistance Levels
Support and resistance levels are key concepts in technical analysis that help traders identify price points where a stock is likely to stop moving in a particular direction.
- Support Level: Refers to a price level where a stock tends to find buying interest, preventing it from falling further. It acts as a floor for the stock price.
- Resistance Level: Represents a price point where a stock faces selling pressure, preventing it from rising further. It acts as a ceiling for the stock price.
Support and resistance levels can help traders determine entry and exit points for trades, as well as set stop-loss and take-profit levels based on historical price movements.
Candlestick Patterns: How To Analyze Stock Charts
When analyzing stock charts, one important aspect to consider is candlestick patterns. These patterns provide valuable insights into market sentiment and can help investors make informed decisions.
Key Candlestick Patterns
- The Hammer: This pattern indicates a potential reversal to the upside. It consists of a small body and a long lower shadow, suggesting that buyers have stepped in to push prices higher.
- Doji: A Doji represents indecision in the market, with opening and closing prices nearly equal. It can signal a potential reversal if it occurs after a strong trend.
- Bullish Engulfing: This pattern occurs when a large bullish candle completely engulfs the previous bearish candle. It suggests a shift in momentum to the upside.
Interpreting Bullish vs. Bearish Patterns, How to analyze stock charts
- Bullish Candlestick Patterns: These patterns indicate strength and potential upward movement in stock prices. They often signal buying opportunities and positive market sentiment.
- Bearish Candlestick Patterns: Conversely, bearish patterns suggest weakness in the market and potential downward movement in stock prices. They can be used to identify selling opportunities and negative market sentiment.
Market Sentiment Indications
- Combining various candlestick patterns can provide a comprehensive view of market sentiment. For example, a series of bullish patterns may indicate a strong uptrend, while a mix of bullish and bearish patterns could signal indecision or a potential reversal.
- Understanding candlestick patterns and their implications can help traders anticipate market movements and adjust their strategies accordingly.
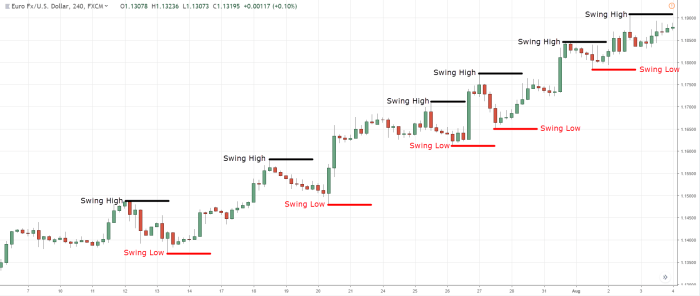
Trend Analysis
In stock chart analysis, trend analysis plays a crucial role in helping investors make informed decisions about buying or selling stocks. By identifying trends, investors can anticipate potential price movements and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Identifying Trends
- An uptrend is characterized by higher highs and higher lows on a stock chart. This indicates that the stock price is generally increasing over time.
- A downtrend, on the other hand, is marked by lower highs and lower lows. This shows that the stock price is decreasing over a period.
- A sideways trend, also known as a range-bound market, occurs when the stock price moves within a specific price range without a clear upward or downward direction.
Determining Trend Strength
- One technique to determine the strength of a trend is to look at the volume of trading activity. A strong uptrend with increasing volume suggests a healthy market sentiment supporting the price rise.
- Another indicator is the moving averages, where the price consistently stays above or below a specific moving average line. This can indicate the strength of the trend in a particular direction.
- Additionally, trendlines can be drawn on a stock chart to connect swing lows in an uptrend or swing highs in a downtrend. The angle and steepness of these trendlines can provide insights into the strength of the trend.
