Get ready to dive into the world of dividend stocks strategies, where we break down the essentials in a way that’s easy to digest. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting out, this guide will equip you with the knowledge you need to make informed decisions.
Introduction to Dividend Stocks
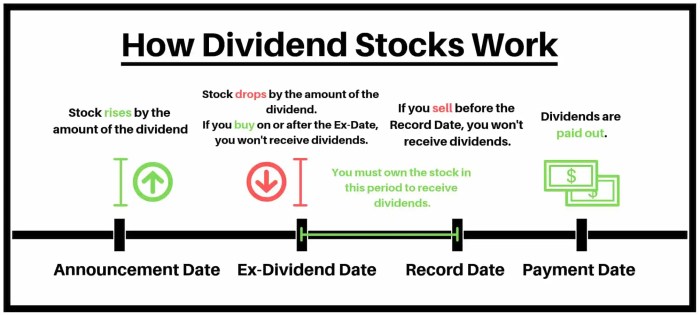
Dividend stocks are shares of companies that pay out a portion of their profits to shareholders on a regular basis. The purpose of including dividend stocks in an investment portfolio is to generate a steady income stream, in addition to any potential capital appreciation.
Benefits of Dividend Stocks
- Stable Income: Dividend stocks provide a reliable source of income, making them attractive for investors seeking regular payouts.
- Lower Volatility: Companies that pay dividends are often more established and stable, which can help reduce the overall volatility of a portfolio.
- Historical Performance: Dividend-paying stocks have historically outperformed non-dividend-paying stocks over the long term.
Difference from Growth Stocks
Dividend stocks differ from growth stocks in that they prioritize income generation over capital appreciation. While growth stocks reinvest their profits into the company for future growth, dividend stocks distribute a portion of their profits to shareholders.
Choosing Dividend Stocks
When it comes to selecting dividend-paying companies, there are several criteria to consider. One of the key factors to look at is a company’s dividend history. This can give you insights into how consistent and reliable their dividend payments have been over time. Additionally, analyzing a company’s financial health is crucial before investing in dividend stocks to ensure they have the ability to sustain and grow their dividend payouts.
Criteria for Selecting Dividend-Paying Companies
- Stable and consistent dividend payments
- Strong track record of dividend growth
- Healthy balance sheet with manageable debt levels
- Positive cash flow and earnings growth
Importance of Looking at a Company’s Dividend History
Examining a company’s dividend history can provide valuable insights into their financial stability and management’s commitment to rewarding shareholders. A company with a long history of paying dividends and increasing them over time is generally viewed as a positive sign.
Analyzing a Company’s Financial Health
Before investing in dividend stocks, it is essential to assess a company’s financial health. This includes looking at key financial metrics such as:
- Revenue and earnings growth
- Debt levels and debt-to-equity ratio
- Free cash flow
- Profit margins
Remember, a company’s ability to generate consistent cash flow is critical for sustaining dividend payments.
Strategies for Investing in Dividend Stocks
When it comes to investing in dividend stocks, there are various strategies that investors can consider. Two popular strategies include Dividend Growth Investing and Dividend Value Investing. Additionally, utilizing Dividend Reinvestment Plans (DRIPs) can provide benefits for long-term investors. Let’s explore these strategies in more detail.
Dividend Growth Investing
Dividend Growth Investing focuses on investing in companies that have a history of increasing their dividend payouts consistently over time. This strategy appeals to investors looking for steady income and potential capital appreciation. By selecting companies with a strong track record of dividend growth, investors can benefit from compounding returns and potentially higher yields in the future.
Dividend Value Investing
Dividend Value Investing involves identifying undervalued dividend-paying stocks that have the potential for price appreciation. Investors following this strategy look for companies with stable cash flow, low debt levels, and attractive valuations. By purchasing these stocks at a discount, investors can potentially benefit from both dividend income and capital gains as the market corrects the undervaluation.
Dividend Reinvestment Plans (DRIPs)
Dividend Reinvestment Plans (DRIPs) allow investors to automatically reinvest their dividend payouts back into additional shares of the company’s stock. This can help investors take advantage of compound growth over time, as dividends are reinvested and can generate additional income. DRIPs are particularly beneficial for long-term investors looking to maximize their returns through consistent reinvestment of dividends.
Individual Dividend Stocks vs. Dividend-Focused ETFs
When deciding between investing in individual dividend stocks or dividend-focused ETFs, investors must consider the advantages and disadvantages of each option. Investing in individual dividend stocks allows for greater control over the selection of companies and potential for higher dividend yields. On the other hand, dividend-focused ETFs provide diversification across multiple dividend-paying stocks, reducing individual company risk. However, investors may have less control over the specific stocks included in the ETF and may incur management fees.
Risks and Challenges of Dividend Stocks
When investing in dividend stocks, there are several risks and challenges that investors need to be aware of to make informed decisions. Understanding these risks can help investors navigate the market more effectively and protect their investments.
Common Risks Associated with Dividend Stocks
- Market Volatility: Dividend stocks are not immune to market fluctuations, so the value of your investment can go up or down depending on market conditions.
- Dividend Cuts: Companies may reduce or eliminate dividend payments if they are facing financial difficulties, which can lead to a decrease in income for investors.
- Interest Rate Changes: Rising interest rates can make dividend stocks less attractive compared to fixed-income investments, impacting their value.
- Company Performance: Poor company performance can result in lower stock prices and reduced dividend payments, affecting investor returns.
Impact of Economic Conditions on Dividend Payments
- Recession: During economic downturns, companies may struggle to maintain dividend payments, leading to cuts or suspensions.
- Inflation: High inflation can erode the purchasing power of dividend income over time, affecting the real return on investment.
- Interest Rates: Changes in interest rates by central banks can influence company borrowing costs and profitability, impacting dividend payments.
Mitigating Risks when Investing in Dividend Stocks
- Diversification: Spread your investments across different sectors and industries to reduce the impact of poor performance from a single company.
- Research: Conduct thorough research on companies before investing to ensure they have a history of stable dividend payments and strong financial health.
- Monitor: Stay informed about economic conditions and company developments to make timely decisions and adjust your portfolio as needed.
