Ready to dive into the world of Analyzing company stocks? Buckle up as we explore the ins and outs of this financial adventure, breaking down the complexities in a way that’s easy to digest.
Get ready to uncover the mysteries behind analyzing company stocks and how it can impact your investment decisions.
Introduction to Analyzing Company Stocks
Investing in stocks can be a lucrative opportunity, but it comes with risks. Analyzing company stocks is a crucial process that investors undertake to make informed decisions. By examining various aspects of a company’s financial health and market performance, investors can assess the potential risks and rewards of investing in a particular stock.
Analyzing company stocks involves evaluating a company’s financial statements, market trends, industry performance, and overall economic conditions. This comprehensive assessment helps investors gauge the company’s growth potential, profitability, and sustainability in the market.
The Importance of Analyzing Company Stocks for Investors
- Identifying investment opportunities: Analyzing company stocks helps investors identify promising investment opportunities that align with their financial goals.
- Managing risks: By conducting thorough analysis, investors can mitigate risks associated with investing in volatile markets or uncertain industries.
- Maximizing returns: Through careful analysis, investors can make strategic investment decisions that have the potential to maximize returns on their investments.
Key Factors to Consider When Analyzing Company Stocks
- Financial Health: Assessing a company’s financial statements, including revenue, profitability, debt levels, and cash flow, is essential in determining its financial health.
- Market Performance: Analyzing a company’s stock price performance, market share, and competition can provide insights into its position in the market.
- Industry Trends: Understanding industry trends, market dynamics, and regulatory environment can help investors evaluate a company’s growth prospects and competitive advantage.
- Management Team: Evaluating the company’s management team, their track record, and strategic decisions can give investors confidence in the company’s leadership and direction.
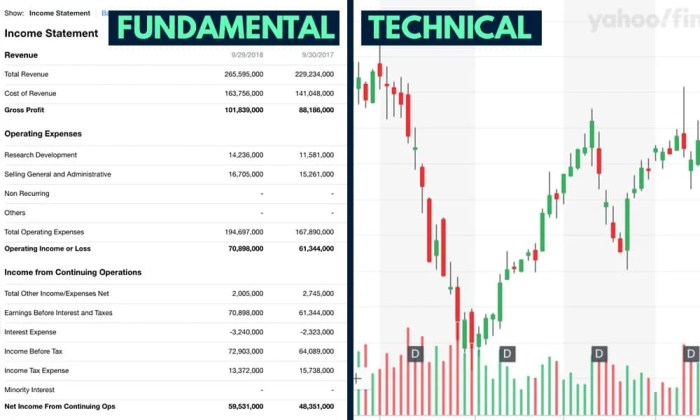
Fundamental Analysis of Stocks
Fundamental analysis of stocks involves evaluating a company’s financial health and performance to determine its intrinsic value. This type of analysis focuses on factors such as revenue, earnings, assets, and liabilities to assess the overall strength of a company.
One of the fundamental analysis tools used in evaluating company stocks is the Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio. This ratio compares a company’s current stock price to its earnings per share (EPS) and helps investors understand how much they are paying for each dollar of earnings.
Another tool is the Debt-to-Equity (D/E) ratio, which shows the proportion of debt a company uses to finance its operations compared to its equity. A high D/E ratio may indicate that a company is taking on too much debt, which could be risky for investors.
Interpreting financial statements during fundamental analysis involves analyzing key financial ratios like the Return on Equity (ROE), which shows how efficiently a company is using its shareholders’ equity to generate profits. A high ROE is generally considered favorable as it indicates strong profitability.
Analyzing Cash Flow Statements
Cash flow statements provide insight into how cash is flowing in and out of a company. It is crucial to analyze a company’s cash flow to understand its ability to meet financial obligations and fund future growth. Key metrics to consider include operating cash flow, investing cash flow, and financing cash flow.
- Operating Cash Flow: This metric shows how much cash a company generates from its core business operations. A positive operating cash flow indicates that a company is able to generate enough cash to cover its day-to-day expenses.
- Investing Cash Flow: This measures the cash used for investments in assets such as property, plant, and equipment. A negative investing cash flow could indicate that a company is heavily investing in its growth.
- Financing Cash Flow: This reflects the cash flow from financing activities such as issuing debt, repurchasing shares, or paying dividends. A positive financing cash flow may indicate that a company is raising capital to fund its operations or expansion.
It is essential to look beyond a company’s earnings and consider its overall financial health when conducting fundamental analysis of stocks.
Technical Analysis of Stocks
When it comes to analyzing company stocks, technical analysis plays a crucial role in predicting price movements based on historical market data rather than the intrinsic value of the company.
Common Technical Indicators
- RSI (Relative Strength Index): This indicator measures the speed and change of price movements, helping investors identify overbought or oversold conditions.
- MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): By comparing two moving averages, MACD helps traders spot changes in the strength, direction, momentum, and duration of a trend.
- Bollinger Bands: These bands indicate volatility and potential price reversals by plotting two standard deviations away from a simple moving average.
- Volume: Monitoring trading volume can confirm price trends, signaling the strength or weakness of a particular move.
Using Charts in Technical Analysis
Charts are essential tools in technical analysis as they visually represent historical price movements and patterns that can help traders predict future stock prices. Different types of charts, such as line charts, bar charts, and candlestick charts, provide valuable insights into market trends, support and resistance levels, and potential entry or exit points for trades.
Valuation Methods for Company Stocks
When it comes to analyzing company stocks, understanding different valuation methods is crucial for making informed investment decisions. Valuation methods help investors determine whether a stock is overvalued, undervalued, or fairly priced based on various financial metrics.
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Analysis
DCF analysis is a valuation method that estimates the value of a company based on its future cash flows. By discounting these cash flows back to present value using a discount rate, investors can determine the intrinsic value of a stock. One of the strengths of DCF analysis is its focus on the future earning potential of a company, providing a comprehensive view of its value. However, a weakness of DCF analysis is its reliance on future projections, which can be highly uncertain and subject to errors.
Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio
The P/E ratio is a popular valuation method that compares a company’s stock price to its earnings per share (EPS). A low P/E ratio may indicate an undervalued stock, while a high P/E ratio may suggest an overvalued stock. One strength of the P/E ratio is its simplicity and ease of use, providing a quick snapshot of how the market values a company relative to its earnings. However, a weakness of the P/E ratio is its inability to account for growth prospects or other factors that may impact a company’s value.
Comparing Valuation Methods
When it comes to investment decisions, it’s essential to consider the strengths and weaknesses of different valuation methods. For example, while DCF analysis provides a detailed look at a company’s future cash flows, it relies heavily on assumptions and projections that may not always be accurate. On the other hand, the P/E ratio offers a quick comparison of a company’s stock price to its earnings, but it may oversimplify the valuation process. Ultimately, investors may use a combination of valuation methods to gain a more comprehensive understanding of a company’s true value and make more informed investment decisions.
Industry and Market Analysis
Industry and market analysis play a crucial role in assessing company stocks. By understanding the broader industry trends and market conditions, investors can make more informed decisions about buying or selling stocks.
Significance of Industry and Market Analysis
Industry and market analysis provide insights into the overall health and growth potential of a company. It helps investors gauge the competitive landscape, potential risks, and opportunities within a specific industry.
- Identifying Growth Opportunities: Analyzing industry trends can help investors identify sectors that are poised for growth, allowing them to capitalize on emerging opportunities.
- Risk Assessment: Understanding market conditions and industry dynamics enables investors to assess the potential risks associated with investing in a particular company or sector.
- Competitive Analysis: Industry and market analysis help investors compare a company’s performance against its competitors, providing valuable insights into its relative strength and weaknesses.
Strategies for Integrating Industry and Market Analysis
Integrating industry and market analysis into stock analysis involves considering both macroeconomic factors and industry-specific trends to make informed investment decisions.
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of industry news, market reports, and economic indicators to stay informed about the latest trends and developments.
- Use Multiple Data Sources: Utilize a variety of sources, including financial statements, industry reports, and market research, to gain a comprehensive understanding of the industry landscape.
- Consider Long-Term Trends: Look beyond short-term fluctuations and consider long-term industry trends to assess the sustainability and growth potential of a company.
