Kicking off with Options trading for beginners, this opening paragraph is designed to captivate and engage the readers, setting the tone american high school hip style that unfolds with each word.
Are you ready to dive into the world of options trading? Buckle up and get ready to learn the ropes of this exciting financial market!
Introduction to Options Trading
Options trading is a type of investing where individuals can buy or sell contracts that give them the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specific price before a certain date. This differs from stock trading, where individuals directly buy or sell shares of a company.
Basic Concepts and Terminologies
- Call Option: A contract that gives the holder the right to buy an asset at a specified price within a specific timeframe.
- Put Option: A contract that gives the holder the right to sell an asset at a specified price within a specific timeframe.
- Strike Price: The price at which the underlying asset can be bought or sold.
- Expiration Date: The date by which the option contract must be exercised or it expires.
Reasons for Choosing Options Trading
- Levarage: Options allow investors to control a larger amount of an asset with a smaller investment.
- Risk Management: Options can be used to hedge against potential losses in a stock portfolio.
- Income Generation: Selling options can be a way to generate income in addition to capital appreciation.
Types of Options
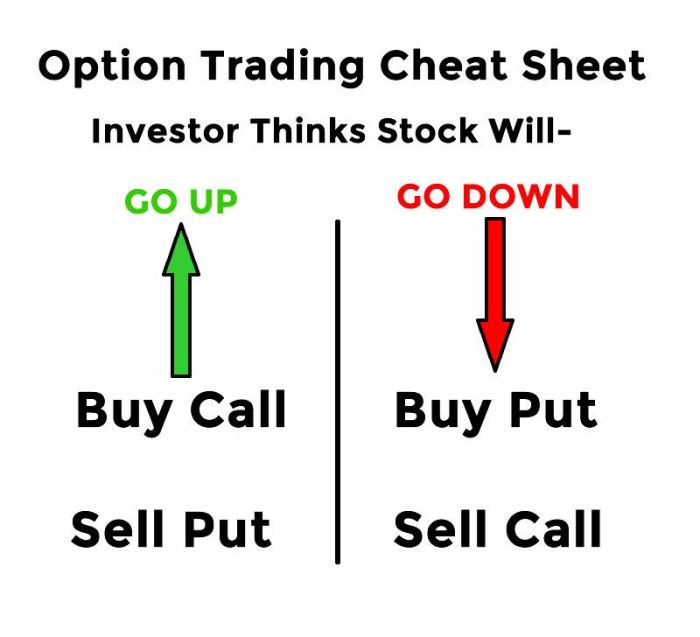
When it comes to options trading, there are two main types of options – call options and put options. Let’s break down the characteristics and risks associated with each type, as well as provide examples of scenarios where they can be beneficial.
Call Options, Options trading for beginners
Call options give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy an underlying asset at a specified price (strike price) within a specific timeframe. The potential risk with call options is limited to the premium paid, but the potential for unlimited profits exists if the underlying asset’s price rises significantly.
- Example: An investor buys a call option on a stock with a strike price of $100. If the stock price rises to $120 within the option’s timeframe, the investor can exercise the option to buy the stock at $100 and sell it at the market price of $120, making a profit.
Put Options
Put options, on the other hand, give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to sell an underlying asset at a specified price (strike price) within a specific timeframe. The potential risk with put options is limited to the premium paid, but the potential for profits exists if the underlying asset’s price decreases.
- Example: An investor buys a put option on a stock with a strike price of $50. If the stock price drops to $40 within the option’s timeframe, the investor can exercise the option to sell the stock at $50, even though the market price is $40, making a profit.
Understanding Option Pricing: Options Trading For Beginners
When it comes to options trading, understanding how options are priced is crucial. There are two main components that determine the price of an option: intrinsic value and time value.
Intrinsic Value and Time Value
Options have intrinsic value if they are in-the-money, meaning the option has actual value based on the price of the underlying asset. On the other hand, time value represents the potential for the option to gain more value before expiration.
Volatility also plays a significant role in option pricing. Higher volatility leads to higher option prices, as there is a greater chance for the underlying asset to move significantly in a short period of time.
Example of Option Pricing
Let’s say you are looking at a call option for a stock that is currently trading at $100. The call option has a strike price of $110 and expires in one month. If the option premium is $5, this means the option has a total value of $5.
Breakdown of the option pricing:
- The intrinsic value of the option is $0 since the stock price is below the strike price.
- The time value of the option is $5, representing the potential for the stock price to increase before expiration.
Strategies for Beginners
When starting out in options trading, it’s important to have a solid understanding of basic strategies that can help you navigate the market. Here, we’ll compare and contrast some strategies like covered calls, protective puts, and long straddles to give you a better idea of how to approach trading options as a beginner.
Covered Calls
A covered call strategy involves selling a call option on a stock that you already own. This can help generate income from the premiums received, while also providing some downside protection in case the stock price falls.
- Buy 100 shares of XYZ stock at $50 per share
- Sell 1 call option with a strike price of $55 for $2 premium
- If the stock price remains below $55 by expiration, you keep the premium and can repeat the process
Protective Puts
Protective puts are used to hedge against potential losses in a stock position. By purchasing a put option, you have the right to sell your shares at a specified price, limiting your downside risk.
- Buy 100 shares of ABC stock at $70 per share
- Buy 1 put option with a strike price of $65 for $3 premium
- If the stock price drops below $65, you can exercise the put option to sell your shares at that price
Long Straddles
A long straddle involves buying both a call and a put option with the same strike price and expiration date. This strategy is used when you expect a significant price movement but are unsure of the direction.
- Buy 1 call option and 1 put option on XYZ stock with a strike price of $60 each
- If the stock price moves significantly above or below $60, one of the options will be profitable while limiting potential losses on the other
Risk Management in Options Trading
When it comes to options trading, managing risk is crucial to protect your investment and maximize potential returns. By implementing effective risk management strategies, traders can navigate the volatility of the options market with confidence.
Importance of Risk Management
- Implementing risk management strategies helps traders mitigate potential losses and preserve capital.
- By setting clear stop-loss orders, traders can limit losses and protect their investment from significant downturns.
- Position sizing allows traders to control the amount of capital they risk on each trade, reducing the impact of any single loss on their overall portfolio.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- One common mistake beginners make is trading without a clear risk management plan in place. To avoid this, traders should establish risk tolerance levels and set stop-loss orders before entering a trade.
- Overleveraging is another pitfall that can lead to significant losses. Beginners should avoid risking more than they can afford to lose on any single trade.
- Failing to diversify a options trading portfolio can expose traders to unnecessary risk. By spreading investments across different assets and strategies, traders can reduce the impact of market fluctuations.
