Diving into the world of risk management in finance, we unravel the complexities and intricacies of how financial institutions navigate the turbulent waters of uncertainty. From understanding the importance of risk management to exploring various strategies and tools, this guide promises to be a thrilling journey through the realm of finance.
Get ready to explore the different facets of risk management in finance and discover how it shapes the financial landscape in profound ways.
Importance of Risk Management in Finance
Effective risk management is crucial in the financial sector to ensure the stability and sustainability of institutions. By identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential risks, financial institutions can protect themselves from uncertainties and unforeseen events that could lead to financial losses.
Benefits of Effective Risk Management
- Improved decision-making: By understanding and managing risks effectively, financial institutions can make informed decisions that align with their risk tolerance and strategic objectives.
- Enhanced financial performance: Proper risk management practices can help institutions optimize their capital allocation, reduce costs, and increase profitability.
- Regulatory compliance: Adhering to risk management guidelines and regulations helps financial institutions maintain compliance and avoid penalties or sanctions.
Consequences of Poor Risk Management
- Financial losses: Inadequate risk management can result in significant financial losses due to unexpected events or market fluctuations.
- Reputation damage: Poor risk management practices can tarnish the reputation of financial institutions, leading to a loss of trust among customers, investors, and stakeholders.
- Lack of resilience: Without proper risk management, institutions may struggle to recover from crises or setbacks, putting their long-term sustainability at risk.
Types of Financial Risks
In the world of finance, there are various types of risks that can impact the stability and success of financial institutions. Understanding these risks is crucial for effective risk management practices.
Credit Risk
Credit risk refers to the potential loss that can occur if a borrower or counterparty fails to meet their financial obligations. This type of risk is commonly faced by banks and other financial institutions that lend money or extend credit to individuals or businesses. For example, if a borrower defaults on a loan, the bank may suffer financial losses and a decrease in profitability.
Market Risk
Market risk is the risk of losses in a firm’s trading portfolio due to changes in market conditions such as interest rates, exchange rates, and commodity prices. This type of risk can impact financial institutions that engage in trading activities. For instance, a sudden change in interest rates can lead to significant losses for a bank holding a large portfolio of fixed-income securities.
Operational Risk
Operational risk arises from the potential for human error, system failures, or external events that can disrupt a firm’s operations. This type of risk can affect financial institutions of all sizes and can lead to financial losses, reputational damage, and regulatory fines. For example, a cyber-attack on a bank’s network can result in data breaches and financial fraud.
Risk Management Strategies
Risk management strategies are essential in finance to minimize potential losses and maximize returns. Various approaches are used to address different types of financial risks, such as risk avoidance, risk mitigation, and risk transfer. Each strategy has its own benefits and drawbacks, depending on the specific situation.
Risk Avoidance
Risk avoidance involves eliminating or withdrawing from activities or investments that carry a high level of risk. This strategy is often used when the potential losses outweigh the potential gains. For example, a company may decide not to invest in a volatile market to avoid significant financial losses.
Risk Mitigation
Risk mitigation focuses on reducing the impact of risks through various techniques such as diversification, hedging, and insurance. By spreading investments across different asset classes or using financial instruments to offset potential losses, organizations can minimize the overall risk exposure. For instance, a company may hedge against currency fluctuations by using forward contracts to lock in exchange rates.
Risk Transfer
Risk transfer involves shifting the financial consequences of risks to another party, such as insurance companies or counterparties. This strategy allows organizations to protect themselves against potential losses by transferring the risk to a third party. For example, a business may purchase liability insurance to cover any damages or legal costs resulting from unforeseen events.
Successful implementation of risk management strategies can be seen in various industries, where companies have effectively navigated volatile market conditions and regulatory changes. By carefully assessing risks and adopting appropriate strategies, organizations can safeguard their financial health and maintain sustainable growth.
Tools and Techniques for Risk Assessment
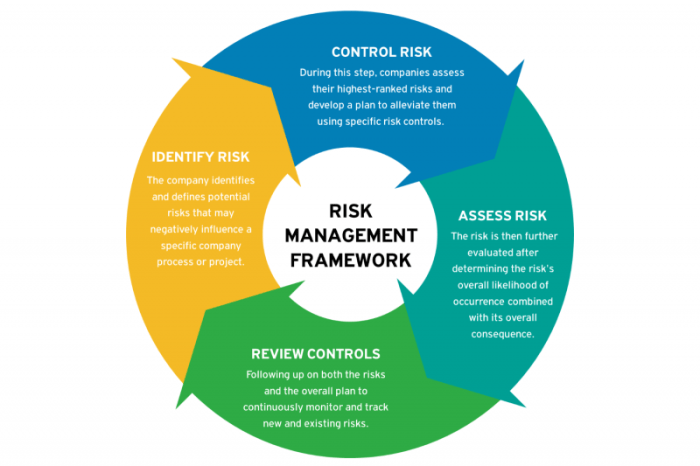
Risk assessment in finance involves the use of various tools and techniques to identify and measure potential risks that may impact financial performance. These tools help financial institutions and investors make informed decisions and develop strategies to mitigate these risks effectively.
Scenario Analysis
Scenario analysis is a technique used to assess the potential impact of different scenarios on financial outcomes. By creating various scenarios based on different assumptions and variables, financial analysts can evaluate the likelihood of each scenario occurring and the potential impact on investments or portfolios. For example, a financial institution may use scenario analysis to assess the impact of interest rate changes on its loan portfolio and identify potential risks.
Stress Testing
Stress testing involves subjecting a financial system or portfolio to extreme conditions to evaluate its resilience and identify vulnerabilities. By simulating adverse market conditions or events, such as economic downturns or market crashes, financial institutions can assess the impact on their assets and liabilities. For instance, a bank may conduct stress tests to determine the effects of a sudden increase in loan defaults on its capital adequacy.
Value at Risk (VaR)
Value at Risk (VaR) is a statistical measure used to quantify the potential loss in value of a portfolio or investment over a specific time period and confidence level. VaR helps investors understand the maximum amount they could lose under normal market conditions. For example, an investment firm may calculate VaR to determine the potential loss of a stock portfolio in a given time frame based on historical data and market volatility.
Regulatory Framework for Risk Management
When it comes to risk management in the financial industry, regulatory frameworks play a crucial role in ensuring that institutions adhere to specific guidelines and requirements to mitigate potential risks.
Regulatory Requirements and Guidelines
Regulatory bodies such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and the Federal Reserve establish rules and regulations that financial institutions must follow to manage risks effectively. These requirements cover areas such as capital adequacy, liquidity management, and reporting standards.
Role of Regulatory Bodies
- Regulatory bodies oversee risk management practices to ensure that financial institutions are operating within the set guidelines.
- They conduct audits and examinations to assess the effectiveness of risk management strategies and identify areas for improvement.
- Regulatory bodies also have the authority to enforce penalties or sanctions on institutions that fail to comply with risk management regulations.
Impact of Regulatory Compliance
- Financial institutions face increased operational costs to meet regulatory compliance standards, which can impact their profitability.
- However, adherence to regulatory requirements helps to enhance transparency, accountability, and stability within the financial system.
- Compliance with regulatory frameworks also builds trust and confidence among investors, customers, and stakeholders.
